Appendix: Architecture of abess¶
In this page, we briefly introduce our core code of abess, which is summarized in the Figure below.
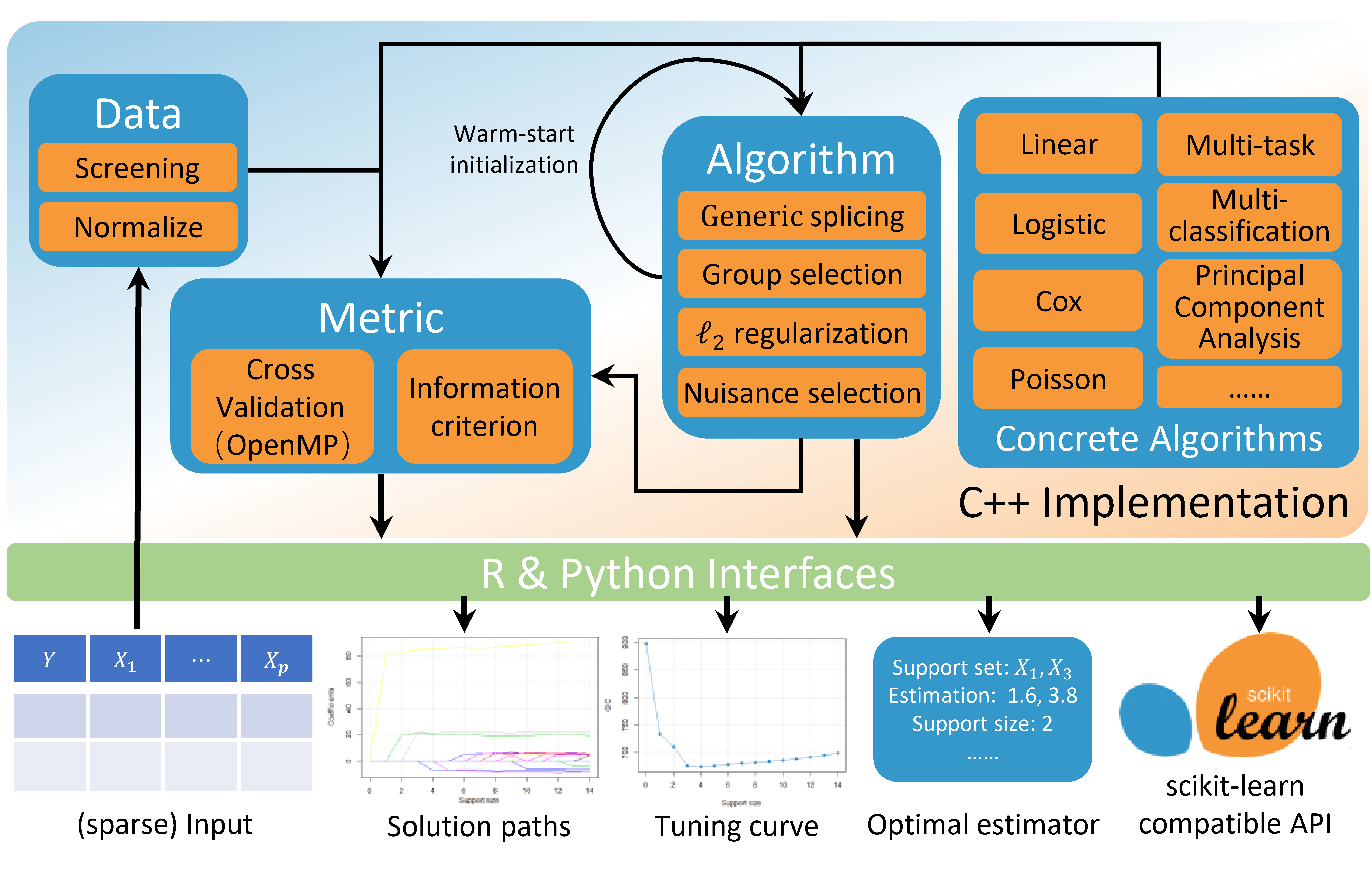
The core code of abess is built with C++ and the figure above shows the
software architecture of abess and each building block will be described
as follows.
The Data class accept the (sparse) tabular data from R and Python interfaces, and returns a object containing the predictors are (optionally) screened or normalized.
The Algorithm class, as the core class in
abess, implements the generic splicing procedure for best subset selection with the support for \(L_2\)-regularization for parameters, group-structure predictors, and nuisance selection. The concrete algorithms are programmed in the subclass of Algorithm by rewriting the virtual function interfaces of class Algorithm. Seven implemented best subset selection tasks for supervised learning and unsupervised learning are presented in the above Figure. Beyond that, the modularized design facilitates users extend the library to various machine learning tasks by writing subclass of Algorithm class.The Metric The serves as a evaluator. It evaluates the estimation returned by Algorithm by cross validation or information criterion like Akaike information criterion and high dimensional Bayesian information criterion.
Finally, R or Python interfaces collects the results from Metric and Algorithm. In R package, S3 methods are programmed such that generic functions (like
print,coefandplot) can be directly used to attain the best subset selection results, and visualize solution paths and tuning parameter curve. In Python package, each model in abess is a sub-class ofscikit-learn's BaseEstimator class such that users can not only use a familiar API to train a model but also seamlessly combine model inabesspreprocessing, feature transformation, and model selection module withinscikit-learn.